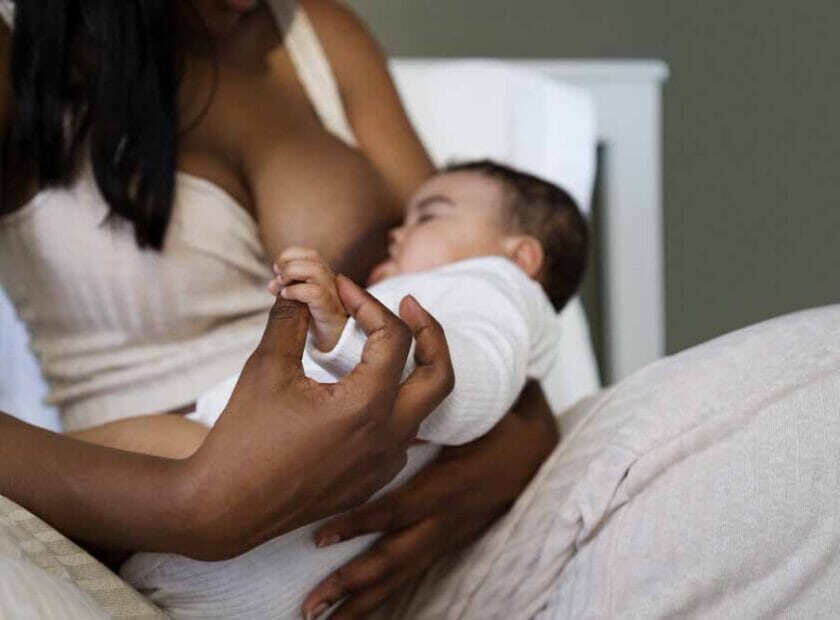
Breastfeeding is highly recommended for infants as it provides the optimal balance of nutrients and antibodies that support a baby’s development and immune system. It offers numerous benefits for both the baby and the mother.
Benefits of Breastfeeding for the Baby
- Optimal Nutrition:
– Breast milk contains the perfect mix of vitamins, proteins, and fats needed for a baby’s growth and development. - Immune Protection:
– Contains antibodies that help protect the baby from infections and diseases, including ear infections, respiratory illnesses, and diarrhea. - Digestive Health:
– Easier to digest than formula, reducing the likelihood of constipation and gas. - Cognitive Development:
– Linked to higher IQ scores and better cognitive performance as the child grows. - Emotional Bonding:
– Physical closeness, skin-to-skin contact, and eye contact during breastfeeding strengthen the emotional bond between mother and baby.
Benefits of Breastfeeding for the Mother
- Promotes Postpartum Recovery:
– Helps the uterus return to its pre-pregnancy size and reduces postpartum bleeding. - Burns Calories:
– Can help the mother lose pregnancy weight faster by burning extra calories. - Lowers Health Risks:
– Reduces the risk of breast and ovarian cancers, type 2 diabetes, and postpartum depression. - Cost-Effective:
– Saves money on formula and feeding supplies. - Convenience:
– Breast milk is always available and at the right temperature, eliminating the need to prepare bottles.
Breastfeeding Recommendations
- Exclusive Breastfeeding:
– The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months of life. - Continued Breastfeeding:
– Continued breastfeeding along with appropriate complementary foods up to two years of age or beyond.
Tips for Successful Breastfeeding
- Start Early:
– Begin breastfeeding within the first hour after birth to help establish a good milk supply. - Proper Latching:
– Ensure the baby is latching on correctly to prevent nipple pain and ensure efficient milk transfer. - Frequent Feeding:
– Feed on demand, typically every 2-3 hours, to maintain milk production and meet the baby’s needs. - Stay Hydrated and Nourished:
– Drink plenty of water and eat a balanced diet to support milk production. - Seek Support:
– Consult with lactation consultants or join breastfeeding support groups for guidance and encouragement.
Common Challenges and Solutions
- Sore Nipples:
– Ensure proper latching, use nipple creams, and allow nipples to air-dry after feeding. - Low Milk Supply:
– Breastfeed frequently, ensure proper latch, and consider pumping between feedings to stimulate production. - Engorgement:
– Feed frequently, use warm compresses before feeding, and cold compresses after feeding. - Blocked Ducts:
– Massage the affected area, apply warm compresses, and continue breastfeeding to clear the blockage. - Mastitis:
– A breast infection that can be treated with rest, antibiotics, and frequent breastfeeding or pumping.
When to Seek Professional Help
- Persistent Pain: If breastfeeding is consistently painful, consult a lactation consultant.
- Low Milk Supply: If you’re concerned about milk supply, seek advice to ensure your baby is getting enough nutrition.
- Baby’s Weight: If the baby is not gaining weight or seems constantly hungry, get a professional evaluation.
- Infection Signs: If you have signs of mastitis, such as fever, chills, and a painful, red area on the breast, seek medical attention.
Key Takeaways
- Natural and Beneficial: Breastfeeding provides the best nutrition and health benefits for both baby and mother.
- Support and Education: Learning about breastfeeding and seeking support can help overcome challenges.
- Healthy Practices: Proper latching, frequent feeding, and taking care of the mother’s health are crucial for successful breastfeeding.
By understanding the importance of breastfeeding and how to address common challenges, mothers can provide their babies with the best possible start in life.